A hiatal hernia develops when a part of the stomach thrusts through the diaphragm and into the chest cavity. This fairly common condition can cause symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing.
What is a hiatal hernia?
The diaphragm is a muscle that helps with breathing by separating the chest cavity from the abdomen. The esophagus, which transports food and liquids from the mouth to the stomach, passes through the hiatus in the diaphragm. When the upper part of the stomach starts pushing through the hiatus and into the chest cavity, it causes a hiatal hernia.
Hiatal hernias are classified into two types: sliding and paraoesophageal. The most common type is a sliding hiatal hernia, which occurs when the esophageal-gastric junction slides up and down through the diaphragm. When a part of the stomach juts through the diaphragm next to the esophagus, this is referred to as a paraoesophageal hernia.
Causes of hiatal hernia
The specific cause of hiatal hernia is unknown; however, several risk factors may contribute to its development. These factors include:
- Age: Hiatal hernias are more prevalent in those aged 50 and older.
- Obesity: The risk of having a hiatal hernia is increased by abdominal pressure caused by excess weight.
- Smoking: Smoking damages the esophageal muscles and can raise the risk of developing a hiatal hernia.
- Pregnancy: Hiatal hernias are more likely to occur during pregnancy because of the added strain an expanding uterus places on the abdomen.
Symptoms of hiatal hernia
Many individuals with hiatal hernias do not exhibit symptoms. Nonetheless, some individuals may have the following symptoms:
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation (when food or stomach acid comes back into the mouth)
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
Treatment of hiatal hernia
Hiatal hernia treatment options depend on the severity of symptoms and the size of the hernia. In mild cases, lifestyle modifications and medication may be enough to manage the symptoms. However, severe cases may require surgery to repair the hernia and prevent future complications.
1. Lifestyle Changes. The first line of defence against hiatal hernia is frequently a change in diet and lifestyle. The following modifications to your lifestyle may effectively reduce your symptoms:
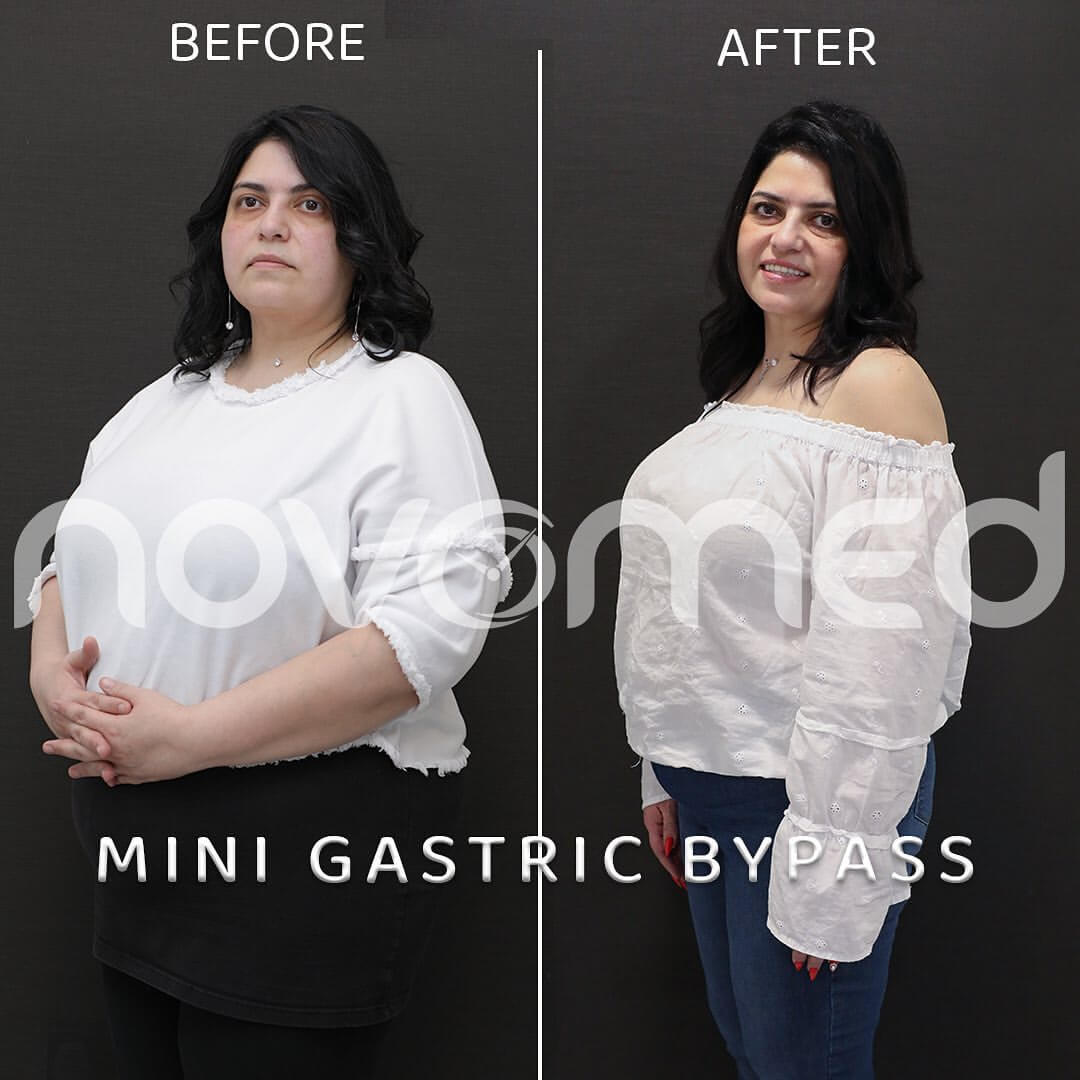
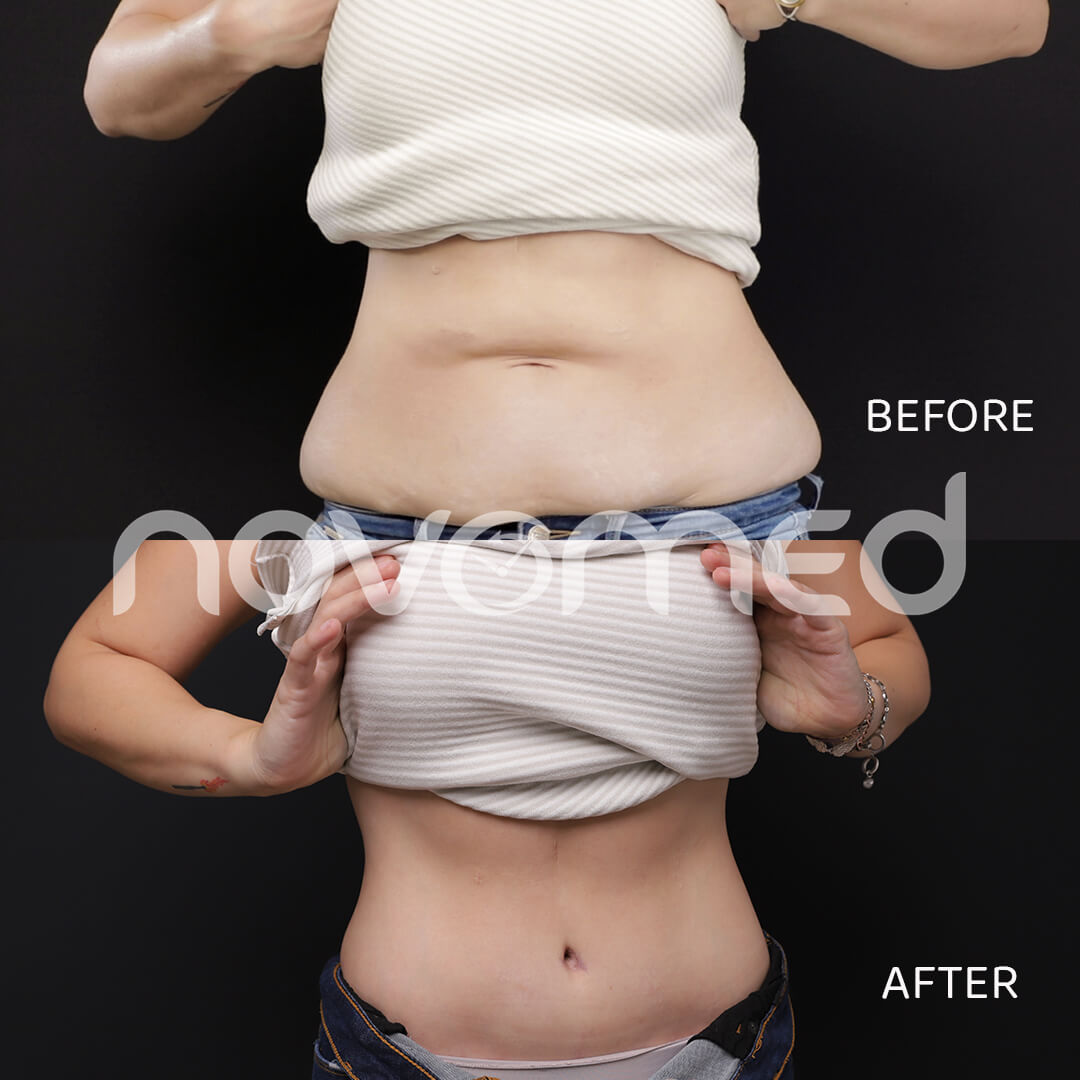
- Weight loss: Excess weight might raise the chance of developing a hiatal hernia by putting strain on the abdomen. Diet and exercise can aid in weight loss, which may help alleviate discomfort.
- Avoid trigger foods: Some food, including fatty or fried foods, spicy foods, and acidic foods, can aggravate symptoms. Avoiding these items may help to alleviate symptoms.
- Eat smaller meals: Consuming smaller, more frequent meals may help alleviate discomfort by decreasing the amount of food in the stomach at once.
- Avoid lying down after meals: Lying down after meals can raise the risk of acid reflux. It is advised to wait a minimum of three hours after a meal before lying down.
2. Medication. Medications such as antacids, proton pump inhibitors, and H2 blockers may be prescribed to help reduce acid reflux.
3. Surgery. In severe cases of hiatal hernia, surgical treatment and prevention of future issues may be required. The most common operation for hiatal hernia is the Nissen fundoplication, which involves wrapping the upper portion of the stomach across the lower esophagus to strengthen the muscle and avoid acid reflux.
Book your consultation at Novomed today!
General Surgeons at Novomed serve patients who require elective or emergency surgical treatments and collaborate with other specialities to offer the finest care for our patients and their families. Our extended consultation hours give you the time you need to address your medical issues, concerns, and questions with our medical professionals.
Book an appointment with the Best General Surgeon by calling our toll-free number 800 (NOVO) 6686 or filling out the booking form below.