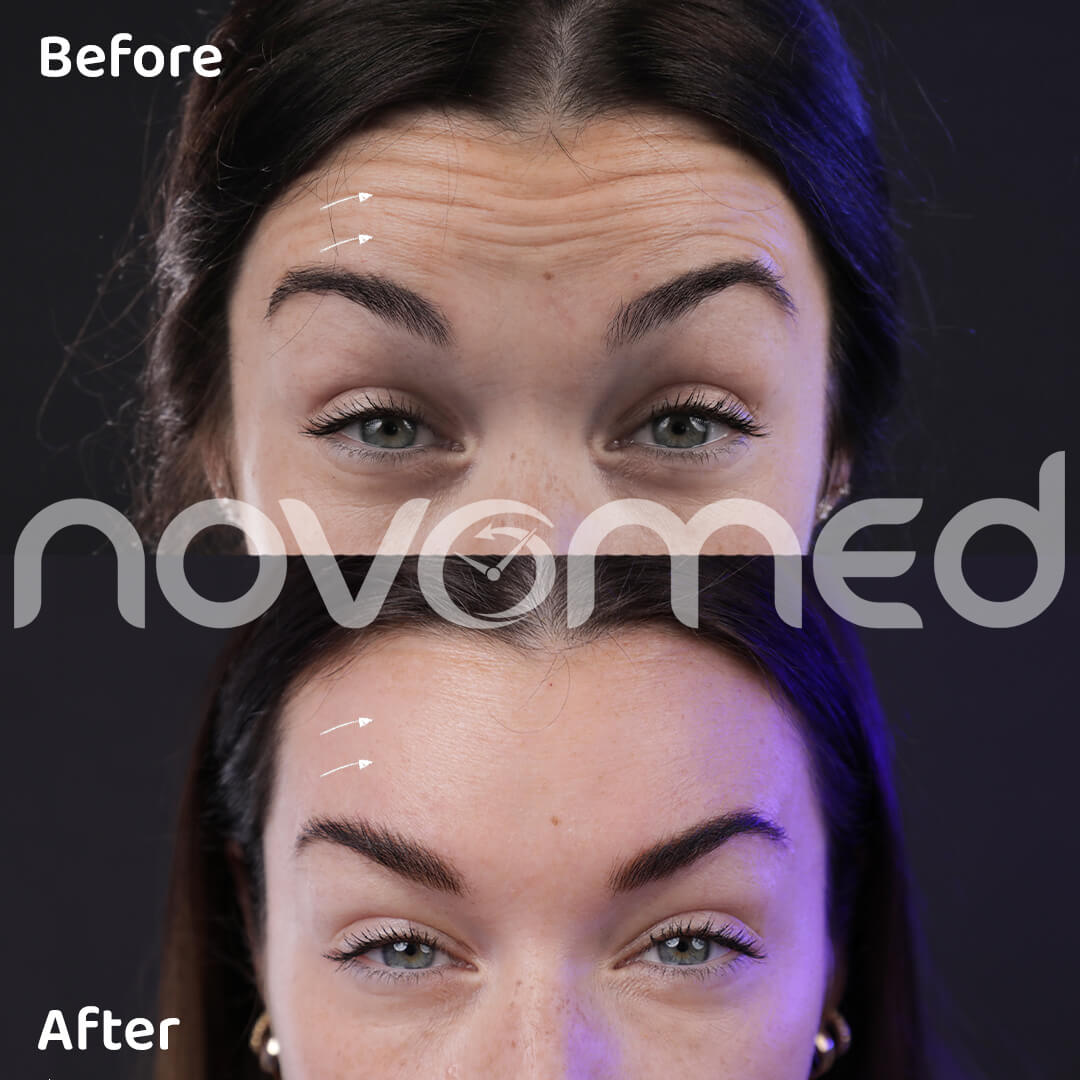
Headaches are a common neurological condition that can cause pain in any part of the head and range from mild to severe. Headache can result from various causes, such as lifestyle factors, genetics, and environmental triggers, and While most headaches are not harmful, some types may indicate a serious underlying condition, leading your doctor to determine that you require immediate medical attention or additional tests.
Symptoms of headache
The symptoms can vary depending on the type and severity of your headache, but common symptoms include:
- Pain in the head or neck area
- Sensitivity to light, sound, or smells
- Nausea or vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Muscle tension in the neck, shoulders, or scalp
- Irritability and mood swings
- Difficulty concentrating
Types of headache
There are more than 150 different types of headaches; however, these are the most common ones:
1. Tension headaches
This is the most common type of headache experienced by adults and teenagers. Tension headaches are usually described as persistent pain that feels like a tight band around the head or pressure around the temples or back of the head. Stress, bad posture, lack of sleep, or tension in the neck and shoulder muscles are the common causes of tension headaches. Symptoms of these headaches include mild to moderate pain, an aching sensation, and sensitivity to light or noise.
2. Migraine headaches
Migraine headaches are a type of headache defined by extremely painful sensations that are frequently accompanied by additional symptoms like nausea, vomiting, sensitivity to light and sound, and vision problems. They can be incapacitating and impair a person’s ability to carry out daily tasks for several hours to a few days. Migraine headache triggers vary from person to person and may include hormonal changes, certain foods, stress, lack of sleep, and environmental factors.
3. Cluster headaches
Cluster headaches are a rare but severe type of headache that arises in cycles, with periods of highly painful pain followed by pain-free intervals. They are typically felt around one eye or temple and described as stabbing or burning pain that might continue for a few hours or up to 15 minutes. Other signs of cluster headaches may include redness of the eye, a stuffy or runny nose, and agitation.
4. Sinus headaches
Sinus headaches are caused by inflammation of the sinuses. They often occur as a result of sinusitis, an infection or inflammation of the sinuses brought on by allergies, infections, or other factors. Sinus headaches are typically characterized by pain and pressure in the forehead, cheeks, and around the eyes, as well as nasal congestion and discharge.
5. Hormonal headaches
Women may experience hormonal headaches, which are brought on by hormonal changes during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause. These headaches are characterized by throbbing pain, usually on one side of the head, and may come with additional symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and fatigue.
6. Rebound headaches
Rebound headaches, also known as medication overuse headaches, can happen when people overuse pain medications for the treatment of headaches. Overuse of medications such as acetaminophen, ibuprofen, or triptans can result in rebound headaches, which are characterized by recurrent headaches that worsen over time.
7. Cervicogenic headaches
Cervicogenic headaches are caused by neck problems, such as muscle tension, nerve irritation, or problems with the cervical spine. They frequently lead to neck pain that extends to the head, affecting one side of the head or face.
Causes of headaches
Because it’s not always obvious what is triggering the pain signals that your nerves are sending to your brain, it might be difficult to identify the precise cause of your headache.
Common headache causes include:
- Lifestyle factors: Headaches can be caused by some lifestyle choices, including dehydration, stress, insufficient sleep, bad posture, inconsistent meal times, and an excessive intake of caffeine or alcohol.
- Environmental triggers: Exposure to bright lights, loud noises, variations in the weather, and environmental toxins can all trigger headaches. These triggers have the potential to result in headaches by causing sensory overload, inflammation, and other physiological reactions.
- Genetic predisposition: Some people may be more genetically susceptible to headaches than others, so there may be a genetic component to headaches. The probability of developing headaches also rises if a family member has a history of them.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions can also contribute to headaches. These can include sinusitis, hormonal imbalances, neck or spine disorders, and other health conditions. The underlying medical issues can be found and treated to help with the headaches.
- Medication overuse: Rebound headaches or medication overuse headaches can be brought on by frequent or excessive use of specific medications, such as painkillers or migraine medications. The body may become dependent on the medication, leading to withdrawal symptoms as it wears off, which might result in these headaches.
Diagnosis of headache
During your consultation, the doctor will review your medical history and ask about your symptoms to discover the type of headaches you are experiencing. They will then perform a physical examination that may involve checking for any signs of underlying medical conditions, such as high blood pressure, neck stiffness, or neurological deficits. Additional tests or imaging examinations, such as blood tests, CT scans, or MRI scans, may occasionally be ordered to rule out any underlying medical disorders or to further assess the source of the headache.
Treatment of headache
It’s significant to note that different treatment approaches for headaches may be necessary depending on each person’s unique situation, medical background, and pain level. The type of headaches you have, how frequently you have them, and their source will all affect the type of treatment you require. Some people don’t even require medical attention. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to choose the best course of action tailored to the patient’s needs.
Treatment options may include:
1. Medications: The pain and other symptoms of headaches are frequently treated with medications. For mild to moderate headaches, over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen may be helpful. Prescription medications, such as triptans for migraines, analgesics, or other pharmaceuticals formulated for the type of headache, may be advised for more severe headaches.
2. Lifestyle changes: Altering one’s lifestyle can help manage and prevent headaches. Lifestyle changes can include techniques for managing stress, better sleep habits, regular mealtimes, staying hydrated, adopting proper posture, and avoiding triggers like bright lights, loud noises, or strong aromas.
3. Relaxation techniques: Deep breathing, meditation, yoga, and progressive muscle relaxation are all relaxation techniques that can help lower stress and muscle tension as well as promote relaxation, which may help prevent headaches.
4. Biofeedback: To avoid or reduce headaches, people can learn to manage specific bodily functions with the help of electronic devices, such as heart rate or muscle tension.
5. Physical therapy: For headaches brought on by muscle tension, poor posture, or neck or spine disorders, physical therapy may be advised. Physical therapists can offer stretches, exercises, and other methods to strengthen muscles, improve posture, and ease neck and shoulder tension.
6. Botox injections: The FDA has approved Botox injections, generally used for cosmetic purposes, as a treatment option for persistent migraines. Botox is injected into particular muscles in the head and neck to help prevent migraines and lessen the frequency and intensity of headaches.
7. Alternative therapies: Acupuncture, chiropractic adjustments, herbal supplements, and aromatherapy are examples of alternative therapies that some people may find helpful for their headaches. Before attempting any of them, you should speak with a licensed healthcare expert.
8. Psychological counseling: Psychological counseling or therapy may be suggested in certain circumstances, particularly for headaches that are brought on by or made worse by stress, anxiety, or depression. Counseling can assist people in managing their stress, coping with any underlying psychological or emotional issues that may be causing their headaches, and developing coping mechanisms.
Schedule your appointment at Novomed today!
If you are bothered by your headaches, contact one of our knowledgeable dentists by calling toll-free 8006686 or clicking the chat icon at the bottom of the screen to manage them effectively.